What are the 2 types of animal life?Set of all animals, (Animalia), any of a gathering of multicellular eukaryotic organic entities (i.e., as particular from microbes, their deoxyribonucleic corrosive, or DNA, is contained in a layer bound core). They are remembered to have developed autonomously from the unicellular eukaryotes. Creatures contrast from individuals from the two different realms of multicellular eukaryotes, the plants (Plantae) and the organisms (Mycota), in basic varieties in morphology and physiology. This is to a great extent since creatures have created muscles and consequently versatility, a trademark that has invigorated the further improvement of tissues and organ frameworks.
for more articles check the World 50 Best
Creatures overwhelm human originations of life on Earth not just by their size, overflow, and sheer variety yet in addition by their portability, a characteristic that people share. So necessary is development to the origination of creatures that wipes, which need muscle tissues, were for some time viewed as plants. Solely after their little developments were seen in 1765 did the creature idea of wipes gradually come to be perceived.
In size creatures are outshone ashore by plants, among whose foliage they may frequently stow away. Interestingly, the photosynthetic green growth, which feed the open seas, are normally excessively little to be seen, yet marine creatures reach to the size of whales. Variety of structure, rather than size, just encroaches incidentally on human attention to life and in this manner is less taken note. In any case, creatures address 3/4 or a greater amount of the species on The planet, a variety that mirrors the adaptability in taking care of, guard, and proliferation which versatility gives them. Creatures follow essentially every known method of living that has been depicted for the animals of Earth.
Creatures move in quest for food, mates, or shelter from hunters, and this development stands out and intrigue, especially as it becomes obvious that the way of behaving of certain animals isn't so totally different from human way of behaving. Other than out of basic interest, people concentrate on creatures to find out about themselves, who are an extremely late result of the development of creatures.
The Animal Kingdom
Creatures developed from unicellular eukaryotes. The presence of an atomic film in eukaryotes licenses division of the two periods of protein blend: record (replicating) of deoxyribonucleic corrosive (DNA) in the core and interpretation (deciphering) of the message into protein in the cytoplasm. Contrasted with the construction of the bacterial cell, this gives more prominent command over which proteins are created. Such control grants specialization of cells, each with indistinguishable DNA however with the capacity to control finely which qualities effectively send duplicates into the cytoplasm. Tissues and organs can along these lines develop. The semirigid cell walls found in plants and parasites, which oblige the shape and consequently the variety of conceivable cell types, are missing in creatures. On the off chance that they were available, nerve and muscle cells, the point of convergence of creature versatility, wouldn't be imaginable.
A definition of Animal
A trait of individuals from the animals of the world collectively is the presence of muscles and the portability they bear. Portability is a significant effect on how a creature acquires supplements for development and generation. Creatures commonly move, somehow, to benefit from other living organic entities, however some consume dead natural matter or even photosynthesize by lodging advantageous green growth. The kind of nourishment isn't quite as definitive as the sort of portability in distinctive creatures from the other two multicellular realms. A few plants and organisms go after creatures by utilizing developments in view of changing turgor tension in key cells, as contrasted and the myofilament-based versatility found in creatures. Versatility requires the improvement of immensely more intricate faculties and inner correspondence than are tracked down in plants or growths. It likewise requires an alternate method of development: creatures expansion in size generally by growing all pieces of the body, while plants and growths for the most part broaden their terminal edges.
All phyla of the set of all animals, including wipes, have collagen, a triple helix of protein that ties cells into tissues. The walled cells of plants and organisms are kept intact by different atoms, like gelatin. Since collagen isn't found among unicellular eukaryotes, even those framing states, it is one of the signs that creatures emerged once from a typical unicellular predecessor.
The muscles that recognize creatures from plants or growths are specializations of the actin and myosin microfilaments normal to every eukaryotic cell. Hereditary wipes, truth be told, are somehow or another not substantially more complicated than accumulations of protozoans that feed similarly. Albeit the tactile and sensory system of creatures is likewise made of changed cells of a kind ailing in plants and parasites, the fundamental component of correspondence is nevertheless a specialization of a synthetic framework that is tracked down in protists, plants, and organisms. The lines that partition a developmental continuum are seldom sharp.
Versatility obliges a creature to keep up with pretty much similar shape all through its dynamic life. With development, every organ framework will in general increment generally proportionately. Interestingly, plants and organisms develop likewise of their external surfaces, and consequently their shape is truly evolving. This fundamental contrast in development designs makes them interest results. For instance, creatures can seldom forfeit pieces of their bodies to fulfill the hungers of hunters (tails and appendages are incidentally exemptions), while plants and organisms do so all around.
History of Classification
With the exception of maybe for the ownership of collagen, the models utilized above to recognize creatures from different types of life are not outright. The principal lists of creature variety depended on by and large structure and comparability. Aristotle and other early scientists viewed all organic entities as a feature of an extraordinary chain, divisions of which were pretty much inconsistent. The eighteenth century Swedish botanist Carolus Linnaeus separated all creatures into six classes: Mammalia, Aves, Amphibia (counting reptiles), Pisces, Insecta (Arthropoda), and Vermes (different spineless creatures). In the mid 1800s the French zoologist Georges Cuvier perceived that vertebrates were considerably unique in relation to spineless creatures, and he partitioned most animals based on structure and capability into four branches: vertebrates, arthropods (expresses), mollusks, and transmits (animals with spiral balance). Cuvier's divisions shaped the reason for every ensuing arrangement.
Soon after Cuvier's characterization, the French naturalist Étienne Geoffroy Holy person Hilaire framed the significance of homologous designs. Homology is correspondence between highlights brought about by progression of data. Subsequently, a bird's wing is homologous to a bat's wing to the extent that both are forelimbs, however they are not homologous as wings. Homologous designs need not look like one another; for instance, the three bones in the center ear of people are homologous to three bones in the jaw mechanical assembly in fishes in light of the fact that the hereditary and formative data controlling them has been nonstop through developmental change.
Before development was by and large acknowledged, homologies among various creatures, when they were perceived by any stretch of the imagination, were viewed as parts of God's example. Development gave a testable clarification to homologies. Via cautiously following chosen homologies, it has been feasible to show that recently proposed arrangements laid out improper connections dependent exclusively upon structure or capability, or both; for instance, the spiral evenness of starfishes isn't homologous to that of coelenterates (like jellyfish).
Protozoans were once viewed as creatures since they move and don't photosynthesize. Closer review has shown, however, that their development is through nonmuscular structures (cilia, flagella, or pseudopods) and that photosynthesis in them has frequently been lost and acquired. Protozoans don't, in this way, structure a characteristic gathering yet with green growth structure an eukaryotic realm separate from plants and creatures, called Protista.
Like plants and creatures, growths emerged from protists and are presently concurred their very own realm.
Animal diversity
The different appearance of creatures is for the most part shallow; the baffling assortment of known structures, some really peculiar, can be various among a simple about six fundamental body plans. These plans are laid out during the undeveloped progressive phases and breaking point the size and intricacy of the creatures. Balance, number and relative improvement of tissue layers, presence and nature of body holes, and a few parts of early improvement characterize these principal methods of association.
Parazoa: a cellular level of organization
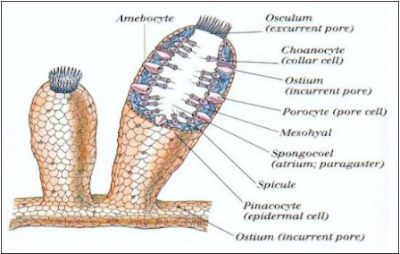
Albeit the two phyla in this subkingdom, Porifera (wipes) and Placozoa, need plainly characterized tissues and organs, their cells practice and coordinate their exercises. Their straightforwardness has been versatile, and wipes have stayed significant in benthic marine environments since their starting point. The sessile, channel taking care of lifestyle shown by wipes has leaned toward a body plan of outspread balance, albeit a few individuals have become lopsided. The state of the crawling, smoothed placozoans is sporadic and inconsistent.
Radiata: a tissue level of organization
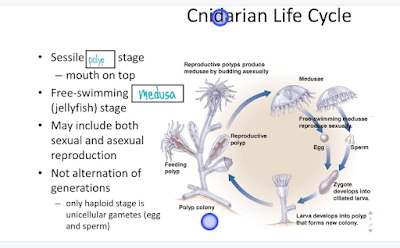
The two coelenterate phyla (Cnidaria and Ctenophora) high level in intricacy past the parazoans by creating beginning tissues — gatherings of cells that are necessarily organized in the presentation of a specific capability. For instance, coelenterates have obvious nerve nets, and their contractile filaments, albeit just particular pieces of additional summed up cells, are coordinated into discrete muscle units. Since discrete cells of various sorts don't complete the inward elements of the creatures, coelenterates are viewed as coordinated at just a tissue level.
The mix of cells into tissues, especially those of nerve and muscle, allows a fundamentally bigger individual body size than is conceivable with different methods of body development. Flagella and cilia become ineffectual at rather little size, and amoeboid development is restricted to the size a solitary cell can accomplish. Muscles contract by a phone system essentially like that utilized in amoeboid movement — cooperation of actin and myosin fibers. Through composed withdrawal of numerous cells, development of enormous people becomes conceivable.
Coelenterates, similar to parazoans, have just two body layers, an internal endoderm fundamentally for taking care of and an external ectoderm for insurance. Between the endoderm and the ectoderm of coelenterates is the mesoglea, a coagulated mass that contains connective filaments of collagen and generally a few cells. The two layers contain muscle filaments and a two-layered trap of nerve cells at the base; the endoderm encompasses a focal pit, which goes from easy to complex in shape and fills in as a stomach, circulatory framework, and once in a while even a skeleton. The depression is additionally utilized for gamete dispersal and waste end.
Cleavage of a treated egg creates an empty circle of flogged cells (the blastula). Invagination of cells at one or the two shafts makes a mouthless, strong gastrula; the gastrula is known as the planula hatchling in species in which this transformative phase is free-living. The inward, endoderm cells accordingly separate to frame the coating of the focal hole. The mouth shapes once the planula hatchling has settled. Albeit the subtleties of early improvement are different for parazoans and coelenterates, most offer a phase in which outside flogged cells invaginate to frame the internal layer, which lines the depression, of these diploblastic (two-layered) creatures. This is normal for invagination during the advancement, everything being equal.
for more articles related Education check the World 50 Best
All coelenterates are pretty much radially balanced. A spiral structure is similarly worthwhile for separating, ruthless, or photosynthetic methods of taking care of. Appendages around the outline can block food this way and that.















0 Comments